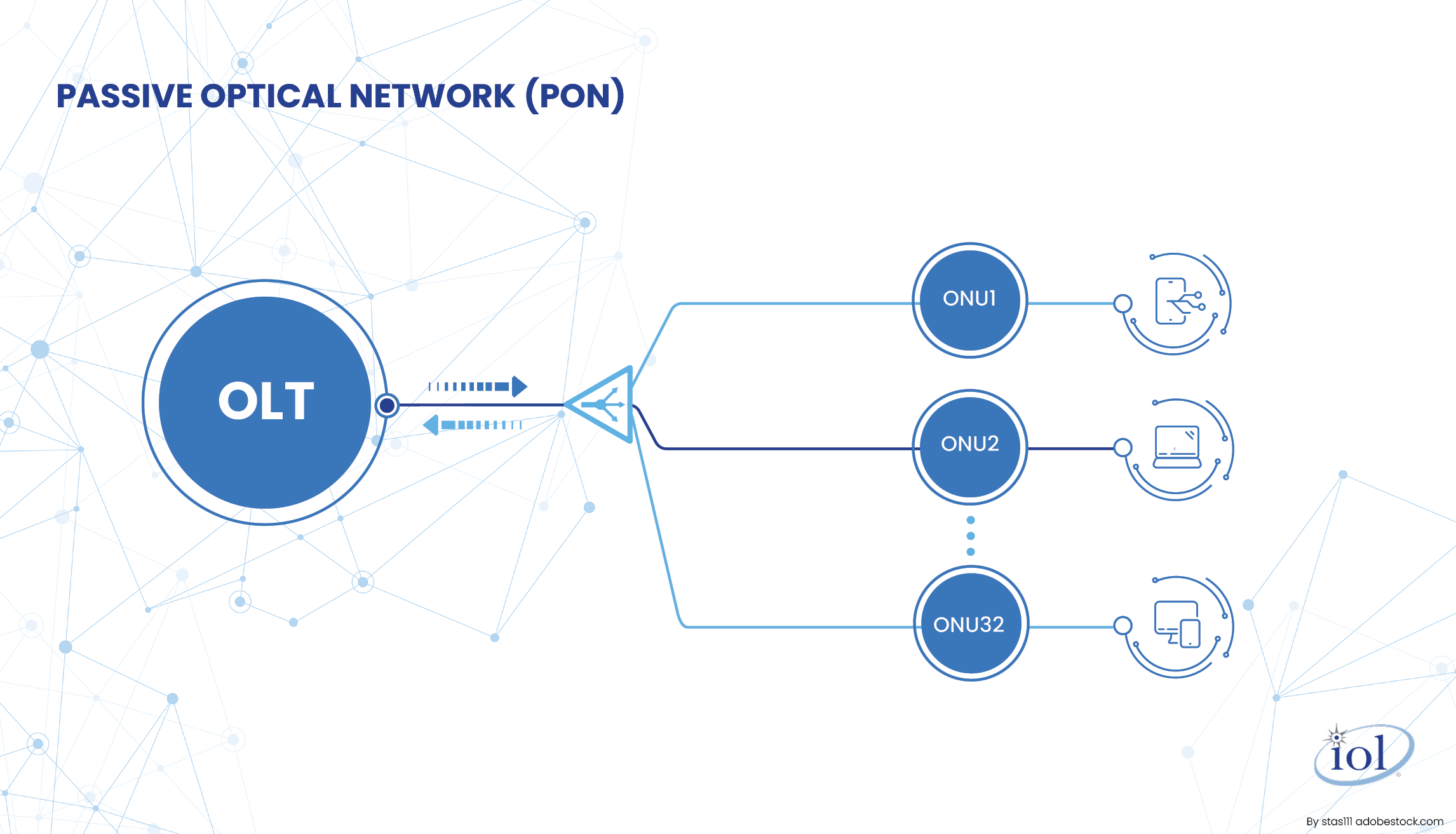
Imagine your internet connection being like a well-orchestrated, optical symphony of speed and reliability. Meet PON, a high-tech communication marvel that uses cutting edge fiberoptics to bring you lightning-fast broadband access. It's not just any network – it's designed to cater to your needs, servicing anywhere from hospitals to high-density residential complexes. PON has revolutionized how we transmit data, enabling high-speed connectivity and efficient delivery of services like Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), video streaming, ultra-bandwidth for HDTV experiences, and online gaming. At the heart of PON is the concept of shared passive optical splitters. Think of them as magic glass prisms that don't need any fancy power sources. They work by dividing the incoming optical signal into multiple outputs, sharing the internet love among different users connected to the PON. No power-hungry electronics here – just a smooth flow of data between the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and the Optical Network Units (ONUs) at your service.
Now, let's delve into the world of PON standards, which are as diverse as they are numerous. GPON, EPON, XG-PON, XGS-PON, NG-PON2, 10G-EPON-the list is enough to make your head spin. The most widely deployed PON standards are published by either the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) or the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). These standards support up to 10 Gbps, with new ones in development that will support 25 Gbps and 50 Gbps. Service providers have the freedom to choose the PON standard that best aligns with their requirements. What sets PON apart? Its passive setup, support for various standards, two-way data flow, scalability, and eco-friendly nature. PON isn't just about speed; it's about a dependable, seamless internet experience that keeps pace with the demands of our digital age – all without straining your budget or the environment.
While DSL and coaxial technologies have served as a reliable means of providing internet access to many users, PON offers significant advantages. Higher speeds, larger bandwidth, less interference due to lack of copper elements, increased range, and power savings all assist PON in making it a superior choice for delivering high-speed broadband services in modern networks.
The system works as a point-to-multipoint system, as shown in the diagram below:
OLT manufacturers' customers are generally the service provider and the end user is the customer of the ONU and ISP.